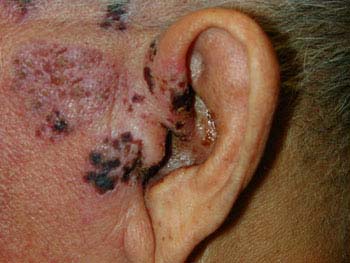
Ear Complications (Herpes zoster oticus):
- Herpes zoster involving the facial nerve produces the Ramsay Hunt syndrome, which is characterized by intense pain in the ear; herpetic vesicles on the external ear or tympanic membrane, mouth, face, neck, and scalp and transitory one-sided facial paralysis.
- This syndrome is occasionally associated with vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing disorder.
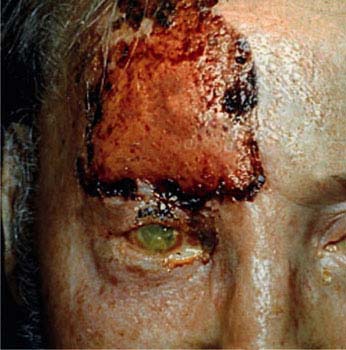
Eye Complications:
These occur when the virus affects the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve.
- Development of corneal surface erosions and ulcerations.
- Decreased sensation of the cornea, decreased tears, late healing and increased risk of corneal injury.
- Increased risk of bacterial infection in the eye
- Zoster uveitis which is a very serious condition that leads to severe eye complaints and pathologies like atrophy of the iris, irregular pupil, corneal edema, formation of cataract and glaucoma too
- Acute retinal necrosis causing blurring of vision and/or pain in one or both eyes.
- In a more severe form, there is absence of light perception and detachment of the retina. This condition has a very poor prognosis.
- Optic neuritis or inflammation of the optic nerve
- Glaucoma usually seen in patients with severe, chronic or repeated attacks of shingles
- Cataract also usually seen in patients with severe, chronic or repeated attacks of shingles
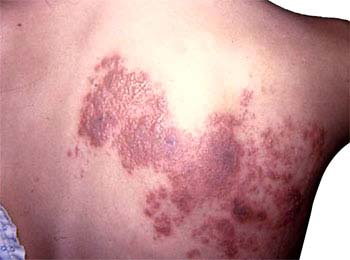
Post Herpetic Neuralgia (PHN):
- Characterized by constant or intermittent continuation of pain that accompanies the acute episode of shingles. This is the most common complication following shingles.
- Especially seen in older and may persist for weeks or months after the sores have healed. The pain can be severe enough to be incapacitating especially in elderly persons.
- In cases of severe or persistent pain, patients can become depressed and on occasions may even become suicidal.
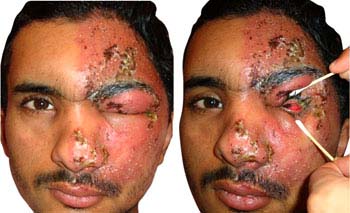
Secondary Infection:
- Secondary bacterial infection of the blisters with streptococci or staphylococci can occur after 1-2 weeks with yellowish crusting or discharge from it.
- Cellulitis is common with the affected area becoming erythematous, tender, firm and hot. Red streaks may appear around the wound.
Central Nervous System Complications:
These usually occur in immunocompromised individuals and include conditions like:
- Meningoencephalitis, i.e., inflammation of brain and its coverings, resulting in delirium, confusion or coma
- Myelitis or inflammation of the outer covering membrane of the nerves
- Cranial nerve palsies or weakness
- Peripheral facial nerve palsy
- Cerebrovascular accident such as stroke
Disseminated or Widespread Herpes Zoster:
This happens in immunocompromised persons leading to involvement of multiple dermatomes, many organs or at times even systemic involvement, causing death due to encephalitis, hepatitis, or pneumonitis.















