COPD is a lung disease which causes obstruction to airflow due to pathological changes occurring in the airways or walls of the air passages and air sacs of the lungs. Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema are the two main conditions associated with COPD. Asthma may or may not be necessarily associated with COPD, but long term untreated Asthma with irreversible damage can end up in COPD.
The normal mechanism of our respiratory system is as follows:
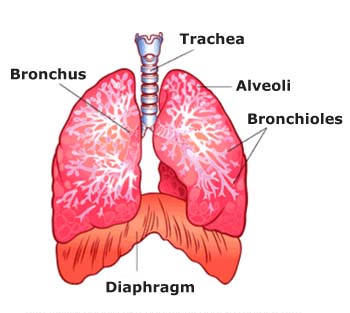
Air inhaled from the nose reaches the lungs through the wind pipe (trachea); the wind pipe then divides into left and right bronchi that enters both the lungs, which further divide into the bronchioles (sub-branches of the bronchus) and end up to form the alveoli (air sacs).
There are around 300 million air sacs in the lungs whose main function is to send pure oxygen in the blood circulation and receive carbon dioxide which can be released during exhalation.
Lungs are the most important organs of the body that help to provide us with life's most essential component, oxygen in its purest form. Lungs expand and contract 20 times in one minute to supply oxygen to the body. Lungs rely on the natural elasticity of bronchi, bronchioles and the air sacs to force impure air out of the body.
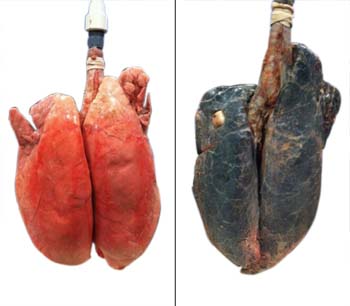
Due to continuous exposure to smoking and air pollution, our sponge-like lungs tend to absorb so many impurities which get stuck and lodged up in these air passages and difficult to be expelled out, leading to various respiratory disorders like COPD.
COPD causes bronchial tubes and air sacs to lose their elasticity and also collapse partially which hampers airflow out of the lungs.
Three main conditions are associated with COPD:
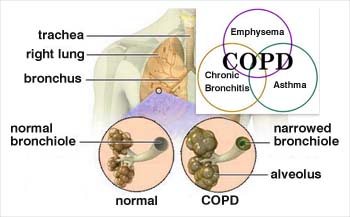
- Chronic Bronchitis: Here, there is inflammation of bronchi and bronchioles which cause increased mucus production along with swelling which could further lead to blockage of bronchial tubes.
- Emphysema: Emphysema is a condition where the alveoli (or air sacs) are damaged resulting in trapping of air within them. As air continues to add up, these sacs enlarge and rupture, or become damaged resulting into a scar tissue. Since these sacs are important for exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide, damage results in less oxygen in blood circulation.
- Asthma: Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways, in which the airways become narrowed leading to breathlessness and cough. Asthma is also included but may not be necessarily associated with COPD.
Homeopathy offers wonderful solutions in the form of carefully selected, dynamized remedies that not only take care of the symptoms of COPD, but also remove the disease right from its roots.
The best part about this is that all this is done at no extra disturbance at the expense of health. Homeopathy is gentle in its touch and has absolutely no side effects in treatment for COPD.















