Clinical Criteria for Diagnosing Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Low back pain and stiffness since a minimum of 3 months that gets better by exercise and not with rest
- Lumbar spine mobility restricted in any direction
- Limitation in chest expansion as compared with normal range for age and gender
Other Indications
-
X-ray of spine & MRI studies: Severe unilateral sacroilitis or moderate bilateral sacroilitis wherein there is inflammation of the hip bones.
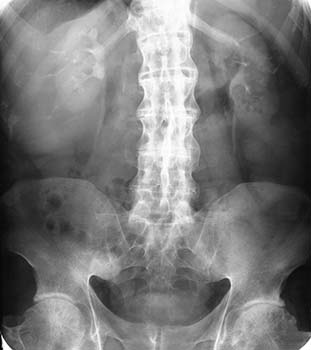
X-ray showing Bamboo Spine
in a patient with Ankylosing Spondylitis - Genetic marker blood tests are the major diagnostic tools. More than 95% of people who have been diagnosed with Ankylosing Spondylitis are HLA-B27 positive.
- C-reactive protein (CRP) and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) increase during acute inflammatory periods but is not seen in everyone.
- The Schober's test is a useful clinical measure performed during examination. Here, the physician tests the ability of the lower back to bend forward effectively. A restriction in forward bending would increase the likelihood of the patient having Ankylosing Spondylitis.















