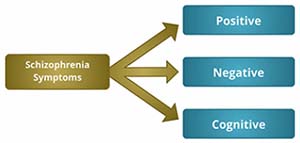
Symptoms of Schizophrenia can be broadly classified in to three broad groups.
POSITIVE SYMPTOMS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA
Positive symptom does not mean a good sign.
Positive Symptoms are thoughts, behaviors or sense perceptions that are overtly present in schizophrenics and absent in a healthy person.
Patients with Positive symptoms of Schizophrenia often lose touch with reality. These symptoms of Schizophrenia occur and disappear. They may be very severe or sometimes hardly noticeable.
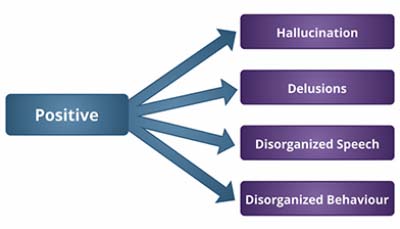
Positive symptoms of Schizophrenia include the following:
-
Hallucinations:
- Hallucinations are altered experiences that occur without a stimulus. A person may see, hear, smell or feel something others cannot. Auditory hallucinations/ Hearing voices are most common.
- Voices often may talk to a person about his behavior or may command him to do something.
- Sometimes voices may even talk to each other.
-
Delusions:
- A delusion is a stubborn idea a patient has despite clear evidence that it is not true. 90% schizophrenics have delusions.
-
Common delusions are:
-
Delusion of persecution: Patient believes that people are watching and following him and plotting against him.
- Delusions of reference: Patient attaches a special and personal meaning to any neutral or unrelated event.
- Delusions of grandeur: Patient sees himself as a very important and great public figure. He may also feel that he is a God.
- Delusions of control: Patient believes that his thoughts and actions are being controlled by external, alien forces.
-
Delusion of persecution: Patient believes that people are watching and following him and plotting against him.
-
Disorganized Speech:
- For a schizophrenic patient, it is unable to concentrate and maintain a train of thought, which is why they may speak incoherently or illogically.
-
Disorganized Behavior:
- A schizophrenic becomes unable to perform activities that are goal-oriented, which disrupt his ability to take care of himself, his work, his interaction with others and even personal hygiene.
- Daily routine and functioning is declined.
- Behaves inappropriately or bizarre which lack purpose.

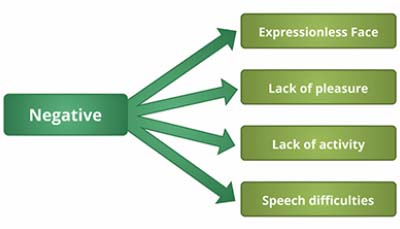
NEGATIVE SYMPTOMS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA:
Negative symptoms of Schizophrenia are those thoughts, behaviors or feelings that are present normally in a healthy individual, but absent in schizophrenics.
To be withdrawn, to be apathetic and to be unable to concentrate can be described as negative symptoms of Schizophrenia as they indicate a reduction in functions and thought processes.
- Lack of expressiveness: The schizophrenic displays a face devoid of, or restricted expressions, no eye-to-eye contact and a flat voice.
- Lack of pleasure: The patient shows complete lack of enthusiasm or motivation. Also there is lack of personal care and hygiene.
- Lack of activity: Patient seems to completely lack an interest in the world; is apparently unaware of his environment and possibly complete social withdrawal.
- Speech difficulties: Patient is unable to maintain or carry out a conversation; answers very shortly or monotonously. This is prominent feature amongst symptoms of Schizophrenia.

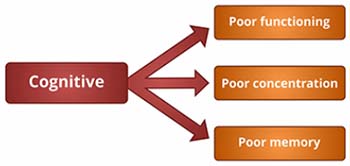
COGNITIVE SYMPTOMS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA:
Cognitive symptoms of Schizophrenia are those that affect the thought process of the individual. They are as following:
- Poor "executive functioning": This implies that a person is not able to understand information and cannot use the same to make decisions.
- Inability to concentrate or pay attention.
- Trouble with "working memory": It means that a person is not able to use information immediately after learning it.
CLASSIFICATION OF SCHIZOPHRENIA
PARANOID SCHIZOPHRENIA- This is a relatively stable type of Schizophrenia, although serious.
- It is characterized by auditory hallucinations and delusions of persecution.
- It is characterized by disorganized thinking, disorganized behavior and blunt and inappropriate emotions.
- The person's ability to function in life is affected.
- There is a tendency to social isolation.
- Two extreme forms are recognized in this type. There may either be an extreme hyper physical activity or completely decreased or stupor condition.
- Excessive mobility may be characterized by moving about excitedly, in frenzy or in circles.
- Physical immobility may be characterized by unable to move or speak, staring and holding the body in a rigid position without being unaware of the environment.
- It is a type of Schizophrenia where some of the symptoms of Schizophrenia from the above types are present, but not enough so as to classify as a particular type.
- It is characterized by at least one episode of Schizophrenia in the past 12 months.
- It may represent a transition between a full blown episode and complete remission.
















