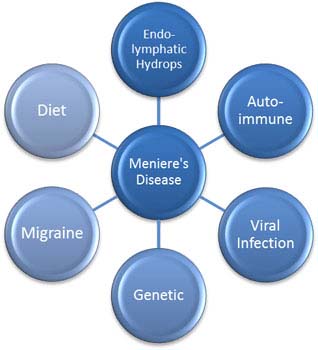
- Excess fluid in the inner ear: The inner ear is a group of connected passages and cavities called a labyrinth. The outside of the inner ear is made of bone (bony labyrinth). Inside is a soft structure of membrane (membranous labyrinth). Normally, there is a presence of fluid in the membrane system of the inner ear.
This fluid plays a very important role in maintaining the balance of an individual. When there is a defect in the membranes of the inner ear like swelling, scarring, infection, injury etc. the fluid bursts out of the membrane entering other areas and causing damage, which affects the sense of balance - Autoimmune: There is some evidence that the body's own immune mechanism may be responsible for the disorder.
- Viral Infection: There is a possibility that virus could be responsible for the disorder.
- Allergies: Any kind of allergy to substances like dust, pollen, or food products like wheat, nuts, dairy products, seafood may trigger inner ear symptoms of dizziness, ringing, hearing loss, etc. and aggravate Meniere's disease.
- Heredity: Meniere's disease could be a result of genetic variation and it could run in families.
- Migraine: There is an increased prevalence of migraine in patients with Meniere's disease. About one third of patients with Meniere's also experience migraines.
- Dietary: There is some evidence that shows excess salt intake can exacerbate the condition.
- Other: Some other probable causes are stress, smoking and alcohol.















