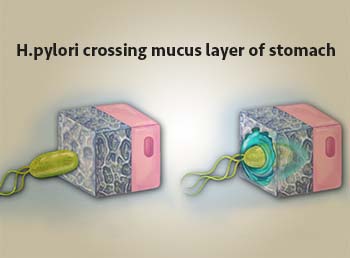
Helicobacter Pylori: Gastric infection with the bacterium H. pylori accounts for the majority of cases of Peptic Ulcer Disease. Transmission of H. pylori occurs from person to person, following an oral-oral or fecal-oral route. This is an important factor among causes of Peptic Ulcer disease.
NSAIDs-induced : Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) are one of the most commonly used conventional medicines. NSAIDs changes surface mucous layer and makes it vulnerable to injury. This is one of the striking causes of Peptic Ulcer disease.
Genetic: Genetic predisposition has also been considered to play a role in ulcer development. First-degree relatives of Duodenal Ulcer patients are three times as likely to develop an ulcer.
Chilies: Capsaicin, the active principle of chilies, causes shedding of surface cells and increases acid secretion when infused in the stomach. Physicians all around the world agree that peptic ulcer is reduced by avoiding chilies.
Tobacco: Cigarette smoking damages mucosal lining of stomach by interfering with protective factors and increases acid secretion. Chronic inflammation of stomach mucosa and ulcers have been noticed in heavy smokers. This is one of the significant causes of Peptic Ulcer disease.
Other causes of Peptic Ulcer Disease: Mental tension, brooding, frustrations and inner resentment related to family matters or place of work predispose an individual to ulcer, also contribute to the perpetuation of symptoms and subsequent recurrences.















